Printing decision is not about deciding on a design, color, layout, test, or size, there comes a huge decision before all that and that is choosing a printing method because there are two popular printing techniques that are equally impressive; and they are – Offset (or traditional printing) and Digital printing. A printing method’s choice directly impacts the result. By comparing both offset and digital printing, we will be able to help you make a more informed decision about where to allocate your printing budget.
Table of Contents
How Important Is It To Choose The Right Digital Printing Vs Offset Printing Method?
Choosing the right offset printing and digital printing method for your print and packaging business is crucial for several reasons:
1. Quality

Different printing techniques yield different qualities of output hence choosing the right method ensures that your designs, colors, and details meet the quality standards expected by your clients.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Each printing method has its cost structure. For large volumes print job, offset printing might be cost-effective, while digital printing might be more suitable for small runs, so choosing the right one ensures you aren’t overspending on production.
3. Speed
Some methods are faster than others. Digital printing, for instance, offers quick turnaround times, which can be crucial for meeting tight deadlines, especially in industries where product launches are frequent.
4. Flexibility
Depending on your business needs, you might require the flexibility to print on various materials. Certain methods work better on specific substrates. Flexography, for instance, is excellent for packaging materials like plastics and cardboard.
5. Customization

If your clients require personalized or variable data printing then offset and digital printing methods are often the best choice. Variable data printing allows you to change elements such as text or images from one printed piece to the next without stopping or slowing down the printing process.
6. Environmentally Friendly Options
Depending on your business needs, you might require the flexibility to print on various materials. Certain methods work better on specific substrates. Flexography, for instance, is excellent for packaging materials like plastics and cardboard.
7. Innovation and Special Effects
Certain printing techniques, like screen printing or letterpress, allow for unique textures and special effects. If your business focuses on premium packaging or specialty products, these two printing methods can add significant value.
8. Brand Image
The quality of your printing reflects directly on your brand. It’s the high-quality, well-printed packaging of the product that prints your brand’s image first on the customer’s mind, leading to the perception of the product, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In short, if you want to stay ahead in the competition, win the hearts and trust of your customers, manage costs, meet deadlines, and establish your brand image, then choosing the appropriate printing method is pivotal. It’s a decision that directly impacts your business’s efficiency, reputation, and bottom line.
Understanding Offset Printing
Large-scale printing projects have relied on offset printing for decades to produce high-quality, consistent results. This printing technique is where ink is transferred from a metal plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. It is called “offset” because the ink is not directly applied to the paper but is transferred first to an intermediate surface. Also known as lithography or lithographic printing, this method is widely used for various printing needs, especially for high-volume commercial jobs.
Offset Printing Setup Process and How It Works
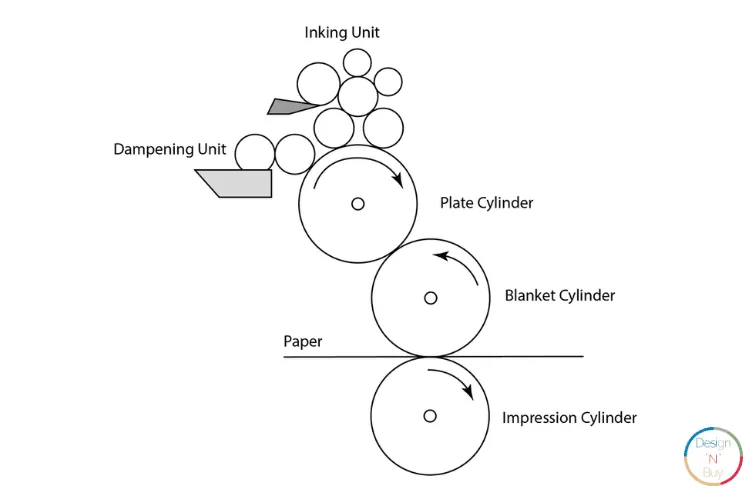
Offset printing setup requires a high initial cost to set up the equipment. However, additional units later become less expensive. Now to begin printing, first off all four custom metal plates typically of CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (key), or of custom ink colors (most notably Pantone colors) are created as per the requirement of the printing job. Offset printing software plays a crucial role in this process, enabling the image or text to be etched onto these metal plates. The areas meant to be printed are raised, while non-printing areas are recessed.
Next, the plate is dampened with water, which adheres to the non-image areas while repelling ink, to ensure that only the image areas attract ink. Further, the ink is applied to the plate, sticking to the raised, image areas. The inked image is transferred from the plate to a rubber blanket, which allows for a smooth transfer of the image. The paper is then pressed between the blanket and an impression cylinder. As the paper passes through, the image is offset onto the paper.
Offset printing is preferred for high-volume projects where cost and quality take priority over setup challenges.
Defining Digital Printing
Digital printing is a modern printing method that saves you from toiling behind creating plates. It directly transfers digital-based images onto a variety of media surfaces. Unlike traditional methods like offset printing, digital printing does not require any manual setup. Instead, it relies on digital files to produce high-quality prints quickly and efficiently. It has gained immense popularity due to its affordability for short runs, variable data printing capabilities, and reduced waste through print-on-demand.
Digital Printing Setup Process and How It Works

Digital printing is a direct-to-print process and hence requires no fancy setup or equipment to be installed, it simply uses either inkjet or laser technology. The digital files of designs are created or prepared digitally using digital printing software, which can be easily edited and transferred to the printing device.
The digital file is then sent directly to the digital printing press, which interprets the digital data and applies the ink or toner directly onto the printing surface, whether it’s paper, fabric, or another material.
After printing, additional finishing processes like cutting, binding, or laminating can be applied, depending on the specific requirements of the print job.
Check our Success Story: Design’N’Buy Web2Print review from Jonas Frisk- Malaysia’s All Inclusive Digital Printing Business
Technologies Used In Offset Printing Vs Digital Printing
Both digital printing and offset printing employ distinct technologies tailored to their respective processes. Here’s a breakdown advantages and disadvantages of offset printing and the key technologies used in each method:
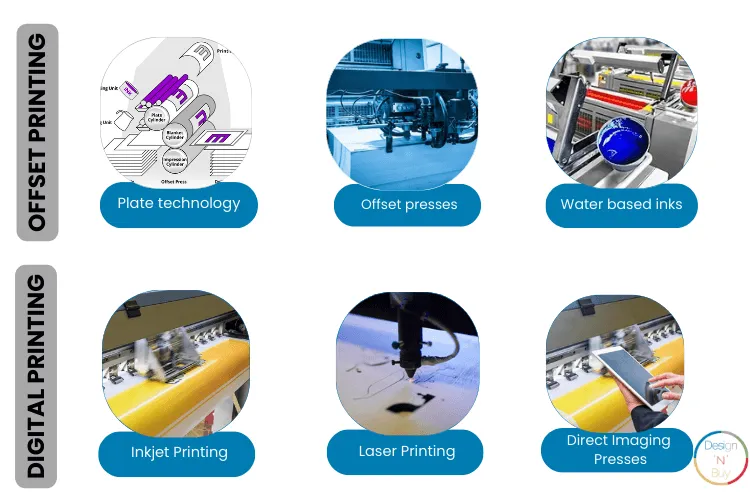
Offset Printing
1. Plate Technology
Offset printing uses metal plates with an image etched onto them. Traditional offset printing often involves aluminum plates coated with photosensitive emulsion. These plates transfer the inked image onto a rubber blanket, which then presses it onto the paper.
2. Offset Presses
Offset presses consist of several cylinders, including plate cylinders, blanket cylinders, and impression cylinders. These cylinders work together to transfer the inked image onto the paper with high precision and consistency.
3. Water-Based Inks
Offset presses consist of several cylinders, including plate cylinders, blanket cylinders, and impression cylinders. These cylinders work together to transfer the inked image onto the paper with high precision and consistency.
Digital Printing
1. Inkjet Printing
Inkjet technology is prevalent in digital printing. It involves propelling droplets of ink onto the printing surface. Inkjet printers are versatile and can handle a wide range of substrates like paper, fabric, and plastic.
2. Laser Printing
Laser printing uses electrostatically charged toner powder, which is fused onto the paper using heat. Laser printers are commonly used for high-speed, high-quality digital printing applications.
3. Direct Imaging Presses
These presses use a digital file to directly image the printing surface without the need for printing plates enabling quick and efficient printing processes, making it ideal for short print runs and variable data printing.
Differences in Technologies used in Offset Printing and Digital Printing
Plate vs. Plateless
Offset printing requires the creation of printing plates, which can be time-consuming and costly for short print runs. Digital printing, on the other hand, is plateless, allowing for quick setup and minimal waste.
Ink Application

In offset printing, ink is transferred from the plate to a rubber blanket before reaching the paper. Digital printing applies ink or toner directly to the printing surface without intermediate steps, allowing for precise and efficient color application.
Versatility
Digital printing offers more substrate options as it can print on various materials without the need for special treatments. Offset printing, while versatile, might require specific types of paper and coatings for optimal results.
Customization
Digital printing excels in customization and personalization due to its ability to print variable data. Offset printing can be customized to some extent, but it’s generally more suited for large, standardized print runs.
Both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different printing requirements and volumes. Hence, the choice between offset printing technology vs digital printing depends on factors such as print volume, customization needs, budget, and desired print quality.
Digital Vs Offset Printing Pros and Cons
Advantages and limitations of Digital printing
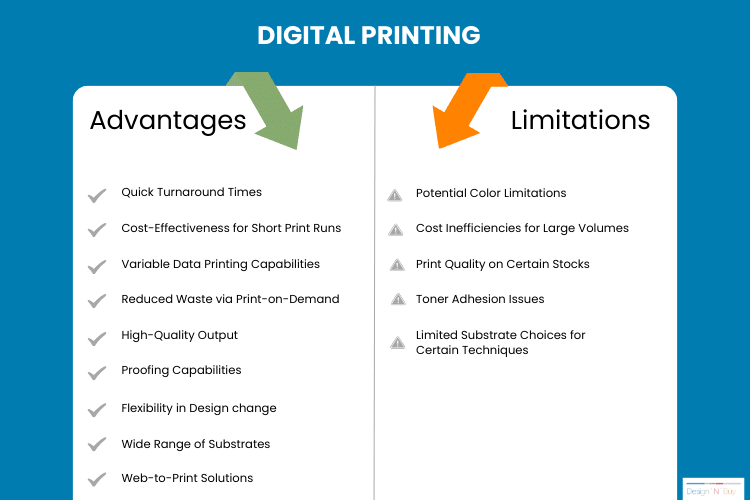
Quick Turnaround Times
Digital printing eliminates the need for lengthy setup processes such as plate creation, allowing for rapid printing, and hence is ideal for projects that require fast delivery.
Cost-Effectiveness for Short Print Runs
Digital printing is economical for short print runs because it doesn’t involve the high setup costs associated with traditional methods. Businesses can print only the quantity they need, reducing excess inventory.
Variable Data Printing Capabilities
Digital printing allows for personalized and variable data printing. Each print can be unique, making it highly suitable for customized marketing materials, direct mail campaigns, and promotional items.
Reduced Waste Through Print-on-Demand

With digital printing, businesses can print on demand, reducing the need for large print runs and minimizing waste. It is environmentally friendly and cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating or unpredictable print needs.
High-Quality Output
Modern digital printing technology produces high-quality prints with sharp text, vibrant colors, and intricate details. Advancements in digital printing have significantly improved print quality, making it suitable for various applications, including marketing collateral and photo books.
Proofing Capabilities
Digital printing allows for easy and cost-effective proofing. Businesses can review digital proof before printing the entire job, ensuring that the final prints meet their expectations in terms of layout, colors, and content.
Flexibility in Design Changes
Digital printing enables on-the-fly design changes without additional setup costs. It helps businesses that frequently update their marketing materials or need to incorporate real-time information into their prints.
Wide Range of Substrates
Digital printing can be done on various substrates, including paper, vinyl, fabric, and more allowing businesses to create a wide range of printed materials, from banners and posters to labels and promotional products.
Web-to-Print Solutions
Digital printing integrates well with web to print platforms, allowing businesses to automate the ordering and printing process. Customers can place orders online, and the printing process can start immediately, streamlining the entire workflow.
Limitations Of Digital Printing
Potential Color Limitations
While digital printing technology has advanced significantly, achieving precise color matching, especially for specific Pantone colors, can be challenging compared to offset printing.
Cost Inefficiencies for Large Volumes
For very large print job runs, digital printing can be more expensive per unit compared to offset printing. Offset printing becomes more cost-effective for bulk quantities due to lower per-piece print job costs.
Print Quality on Certain Stocks
While digital printing is versatile, it may not produce the same level of sharpness and detail on certain textured or specialized papers as offset printing can.
Toner Adhesion Issues

Some digital printing techniques, particularly in toner-based systems, might face challenges with adhesion on certain substrates, leading to issues like cracking or flaking after printing.
Limited Substrate Choices for Certain Techniques
While digital printing can accommodate various materials, some specialty techniques (e.g., embossing, letterpress) are better suited for offset printing due to the specific requirements of these methods.
Advantages and Limitations of Offset Printing

High-Quality Output
Offset printing produces sharp, clean, and high-resolution images, making it ideal for intricate designs and detailed graphics, especially for commercial printing and large format printing requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness for Large Print Runs
Once the setup is complete, the cost per unit decreases for larger print runs, making it economical for mass production.
Versatility in Paper Types
Offset printing can be done on a variety of paper types, including textured, smooth, coated, and uncoated papers, allowing for diverse printing applications.
Pantone Color Matching Capabilities
Offset printing offers precise color matching capabilities, crucial for maintaining consistent brand colors and producing vibrant, accurate prints.
Consistency
Offset printing delivers consistent color and image quality across the entire print run which is crucial for maintaining brand identity and ensuring that every printed piece matches the desired standard.
Specialty Finishes and Inks

Offset printing supports various custom finishes, such as embossing, foil stamping, and spot varnishes, which can enhance the visual appeal of printed materials. Additionally, it accommodates a wide range of inks, including metallic and fluorescent inks.
Durability and Professional Appearance
Offset printing results in durable prints with a professional appearance. The ink penetrates the paper, creating a lasting impression that can withstand handling and environmental factors.
Large Printing Format
Offset presses are available in larger sizes, allowing high-quality printing of oversized materials, such as posters and banners.
Large Format Printing Business Guide
Limitations of Offset Printing
Longer Setup Times
Setting up offset printing involves creating plates and fine-tuning the press, which can be time-consuming, especially for small print jobs. Digital printing, by contrast, has much quicker setup times.
Higher Initial Costs
The initial setup costs, including plate creation and press preparation, can be significant. For small print runs, these costs may not be justifiable compared to the advantages and disadvantages of digital printing.
Waste in Setup Process
Offset printing generates waste during the setup process, including discarded sheets used for calibration and testing. Digital printing, particularly print-on-demand, reduces this type of waste significantly.
Limited Customization for Short Runs

Offset printing is generally less suitable for highly customized or personalized prints in short runs. Digital printing excels in variable data printing and short-run customization.
Environmental Impact
Traditional offset printing often uses petroleum-based inks and involves more chemical processes compared to digital printing, which might not be as environmentally friendly.
Maintenance and Cleanup
Offset presses require regular maintenance and cleanup involving various chemicals, which can be labor-intensive and potentially hazardous if not handled properly.
Remember, a careful evaluation of the pros and cons of two printing methods in the context of the particular printing project is necessary to choose between offset printing vs digital printing.
Factors To Consider For Investment: Offset Printing Vs Digital Printing
Investment is a huge step and therefore before putting all your life savings, there are certain factors to be taken into consideration and they are as follows:
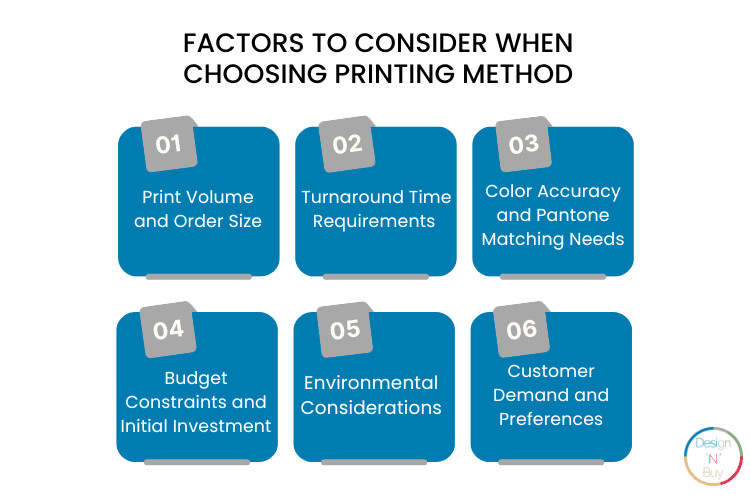
Print Volume and Order Size - How Huge is Your Printing Job?
If you have received large enough print job volumes, then offset should be your choice but if it’s a small to medium-sized print job then digital printing will be the best option as it is cost-effective for small quantities due to minimal setup time and costs.
Turnaround Time Requirements - Is the Clock Ticking?
Longer setup times make offset printing less suitable for urgent orders, on the contrary, digital printing is ideal for projects with deadlines.
Color Accuracy and Pantone Matching Needs - How Visually Effective Do You Want Your Print to Be?
Offset printing offers precise color matching, including Pantone colors, ensuring consistent branding. While advancements have been made in digital and offset printing technology, achieving exact Pantone matches can be challenging. Color accuracy may vary, especially in some digital systems.
Budget Constraints and Initial Investment - How Tight Are You on Your Budget?
Higher initial setup costs make offset printing expensive but economical for large print runs. Whereas, lower setup costs make digital printing suitable for businesses with limited budgets and smaller projects.
Environmental Considerations - Are You a Nature Lover?
Traditional offset printing can involve more chemicals and higher waste due to setup processes but if you have concerns about nature, you must choose digital printing because it offers reduced waste through print-on-demand, making it more environmentally friendly. Some digital printing methods use eco-friendly inks and have a lower environmental impact.
Customer Demand and Preferences - Want to Serve Your Customers What They Ask?
Offset printing is preferred for high-quality, premium products where color accuracy and detail are paramount but customization is difficult in it. Digital printing suits businesses with a focus on quick turnaround, variable data printing, and personalized marketing materials tailored to individual customer preferences.
When print service providers consider these factors, they can make informed decisions about whether to invest in offset or digital printing technologies. Often, a hybrid approach, integrating both technologies based on specific client needs, offers the most versatile and cost-effective solution for many print service providers.
Cost Analysis: Offset Vs Digital Printing
From invisible things like software to huge printing equipment, everything requires money and to ensure that it doesn’t go to waste, here’s a detailed cost analysis for you.
Setup Costs
- Offset printing involves significant setup costs due to the creation of printing plates. The cost varies based on plate material, size, and complexity of the design. It also requires the setting up of an offset press including calibration, ink mixing, paper loading, and skilled labor adding to the setup expenses.
- Digital printing eliminates plate creation costs, reducing initial setup expenses significantly. It does require calibration for color accuracy, but the process is quicker and involves less labor than offset calibration.
Material Expenses
- Paper costs depend on the type, quality, and quantity needed for the print run in offset printing. Offset inks, often oil-based or water-based, contribute to the material expenses.
- Digital printing uses toner or liquid ink. Cost depends on printer type, ink/toner volume, and paper type/quantity.
Labor Costs
- Offset printing requires skilled press operators who handle setup, printing, and maintenance tasks. Labor is needed for finishing processes such as cutting, binding, and quality control.
- Digital printing presses too require skilled operators, though the setup process is quicker and requires less expertise than offset printing. Labor for finishing processes, including cutting and binding, is still required.
To put it simply, offset printing incurs higher costs for setup but is a cheaper option for high-volume digital vs offset printing due to lower per-unit costs. Digital printing is cost-effective for short to medium runs due to minimal waste and print-on-demand capabilities.
Comparison of Offset and Digital Printing
Feature
Digital Printing
Offset Printing
Technology
Utilizes advanced digital inkjet or electrophotographic methods
Uses traditional mechanical printing with ink and plates
Setup Time
Quick setup with minimal preparation and no need for plates
Longer setup time due to plate creation and press calibration
Print Volume
Ideal for short to medium print runs
Economical for large print volumes
Customization
Excellent for variable data and personalized printing
Limited customization options for short runs
Color Accuracy
Good color accuracy, especially with advancements in technology
Precise color matching, including Pantone colors
Speed
High-speed printing suitable for rapid production
Slower setup but high-speed printing once set up
Quality
High-quality prints, especially for digital presses with advanced features
Excellent print quality, especially for detailed designs
Substrates
Versatile, can print on various materials including paper, plastic, fabric, and more
Primarily suitable for paper-based materials
Cost-efficiency
Cost-effective for short to medium runs due to minimal setup costs
Economical for large quantities due to lower per-unit costs
Special Finishes
Limited options for specialty finishes
Offers a wide range of specialty finishes like embossing, foiling, etc
Waste Generation
Low waste generation due to print-on-demand capabilities
Setup processes generate waste; not ideal for minimal print runs
Sustainability
Can be eco-friendly with the use of eco-solvent inks and recycled substrates
Traditional offset printing might use petroleum-based inks; waterless offset printing is more environmentally friendly
Applications
Labels, packaging, textiles, signage, personalized marketing materials
Newspapers, magazines, books, high-end marketing materials, and other printing works
Environmental Impacts: Digital Printing Vs Offset Printing

Both methods have environmental implications. Offset printing uses petroleum-based inks and chemicals, which can be harmful to the environment. Ink cleanup and disposal processes can contribute to pollution. It also requires a significant amount of water, primarily in the dampening process, leading to water wastage. Setup processes and calibration prints in offset printing can lead to paper wastage, especially in smaller print runs.
On the other hand, the production and disposal of toner and ink cartridges in digital printing, especially if not recycled properly, can contribute to electronic waste. Digital printers require energy for both printing and the equipment’s operation, impacting electricity consumption. While digital printing reduces paper waste through print-on-demand, substrate waste occurs when non-paper materials are used.
Best Practices for Two Offset vs Digital Printing Methods
- Minimize setup waste, calibrate accurately, and print only what is needed to reduce paper waste.
- Use eco-friendly inks made from sustainable materials, vegetable oils, or water-based solutions
- Implement recycling programs for paper, plastics, inks, and other consumables to reduce landfill waste.
- Use energy-efficient lighting and equipment in the printing facility to reduce overall energy consumption.
- Educate employees about eco-friendly practices and the importance of sustainability, encouraging a culture of environmental responsibility.

By adopting these eco-friendly options and best practices, both offset and digital printing technologies can significantly reduce their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable printing and packaging industry. Businesses can make informed choices based on these practices to minimize their ecological footprint while meeting their printing needs.
Future Trends In Digital And Offset Printing
- Continuous improvements in inkjet technology lead to higher resolution, faster printing speeds, and a broader range of compatible materials in digital printing.
- While primarily used for prototypes and specialized applications, 3D printing is evolving. As it becomes more accessible and cost-effective, it might impact traditional printing for certain products.
- Continued development of sustainable printing options like water-based inks and biodegradable materials will drive eco-friendliness in offset and digital printing.
- Future printers will be designed for energy efficiency, reducing carbon footprint.
- Growing demand for personalized products, including packaging, marketing materials, and promotional items, will favor digital printing due to its ability to efficiently handle variable data printing.
- Advances in digital technology will enable cost-effective mass customization, allowing businesses to offer unique products at scale driving digital printing adoption for various applications.
- The rise of e-commerce and demand for quick delivery will continue to fuel the need for on-demand printing. Digital printing’s ability to produce small quantities efficiently positions it favorably in this trend.
- Printed materials might incorporate AR elements, enhancing interactivity and user engagement. Both printing technologies can complement AR applications, enabling immersive experiences.
- Embossing, debossing, foiling, and other specialty finishes will continue to be popular. These techniques can be applied to both digital and offset prints, adding value and differentiation to products.
- Hybrid printing solutions that integrate digital and offset processes will become more prevalent. Print service providers might combine the efficiency of digital printing for short runs with the cost-effectiveness of offset printing for bulk production, offering versatile and competitive services.
In the future, both digital and offset printing methods will coexist and evolve to meet the demands of various industries. Print businesses that strategically invest in these technologies, adapt to emerging trends, and offer a blend of traditional quality and innovative solutions will remain competitive in the dynamic printing landscape.
Stay Ahead of the Curve: Empower Your Print Business with our Future-Ready Web to Print Software
Final Thoughts
Now you understand what is offset printing vs digital printing. Offset printing, with the assistance of offset printing software, offers high-quality output, cost-effectiveness for large volumes, precise color matching, and versatility in paper types. It’s ideal for long print runs, consistent branding, and premium products. However, it involves longer setup times and higher initial costs.
Digital printing provides quick turnaround times, cost-effectiveness for short print runs, variable data printing capabilities, reduced waste through print-on-demand, and flexibility in customization. It suits low-volume jobs, personalized marketing materials, and projects with tight deadlines. However, there might be challenges with precise color matching, especially for specific Pantone colors.
FAQ
Most Frequently Asked Questions and Their Answers
Digital printing is a process of printing digital files onto various materials without traditional printing plates. Whereas, offset printing involves transferring an inked image from a plate to a rubber blanket onto the printing surface.
The quality of both digital and offset printing can be excellent. However, the choice depends on the specific project requirements. Generally, offset and digital printing provides higher image quality, especially for high-volume projects, due to its ability to produce precise color matching and consistency.
Digital printing is often considered more eco-friendly because it generates less waste and allows on-demand printing, reducing the need for large print runs. Offset printing requires the creation of printing plates, chemicals, and excess paper waste in the setup process.
Digital printing can be more cost-effective for small to medium-sized print runs because it doesn’t require the setup costs associated with offset printing plates. However, for very large print runs, offset printing becomes more economical due to its lower per-unit cost.
Large print runs, precise color matching (such as Pantone colors), special finishes (like varnishes or embossing), and projects where high image quality and consistency are crucial; offset printing is advised. For short print runs, variable data printing (where each piece can be customized), quick turnaround times, and projects that require cost-effectiveness for small quantities, digital printing will be the best option.
Digital printing allows for quick turnaround times as there’s no need for extensive setup. Files can be printed almost immediately, making it ideal for projects with deadlines and last-minute changes.
Do you have any more questions? Contact our experts
If you’re looking for content related to printing methods, you can consider the following topics: